psoriasis- one of the most common diseases, the frequency of which in the population is constantly increasing every year. And if we take into account that absolutely all age categories are susceptible to this pathology and its simple form quickly flows into a more complex one, then the issue of proper therapy and prevention is really very acute.
According to statistics, approximately every 30 inhabitants of the planet suffers from this disease to one degree or another. What should you do for those who get psoriasis? What folk remedies and remedies can be treated? How to properly organize your meals? Let us finally decide all the points.
Psoriasis and its causes
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease with a rather unclear etiology - the exact cause, despite numerous studies in this field, is still unknown. It is believed that this pathology is a consequence of genetically determined changes in the immune system, as a result of which chronic inflammation of the skin develops. However, its multifactorial nature is also not excluded - in other words, inclusion, along with heritage, and the impact of the external environment.
It is worth noting that predisposing factors, according to scientists, are quite different for different age groups: for example, if different types of bacterial infections, including, in particular, streptococcal infections, are considered to cause causes in children, then foradults, stress stimuli and nicotine abuse are essential, and alcohol, overweight, and the use of certain medications (e. g. , adrenaline receptor blockers).
It is impossible to completely cure psoriasis, however, modern medicine is quite capable of significantly facilitating the course of the disease and maintaining a long-term remission of the patient.
There are several theories to explain the occurrence of psoriasis:
- infectious and parasitic;
- neurogenic;
- endocrine;
- metabolic;
- immunological;
- hereditary;
- theory of molecular mimicry.
As with many other conditions, the cause of skin problems must be found in the gut. Its length is from 4 to 6 meters, and the inner surface is covered with villi, the total surface of which is comparable to the size of a tennis court - this allows the suction processes to proceed much more efficiently. Interestingly, the cells of the small intestinal mucosa are completely renewed every 3-5 days. Here, moreover, up to 70% of human immunocytes are concentrated. So one of the most common causes of psoriasis is considered to be leaky gut syndrome (LEPS).
Deviation from the normal functioning of the intestinal mucosa is fraught with malabsorption, i. e. a violation of the assimilation of essential nutrients (proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals). In addition, the negative impact on the body of toxins and allergens increases: in such conditions, it is much easier for them to enter the bloodstream. The direct link between psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease has been proven in numerous studies.
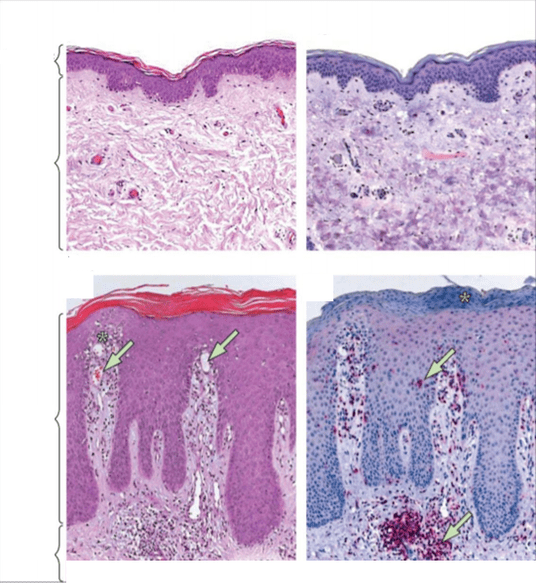
Other scientific works confirm that a special microflora is formed in the skin of a patient with psoriasis, which is significantly different from the microbiome of healthy skin.
In the area of psoriatic lesions, a mass of different bacteria is concentrated, the persistence of which is significantly lower than that of normal skin - in particular, colonization by Staphylococcus aureus is observed, which has an extremely negative effect on the course of the inflammatory process. .
Types of psoriasis
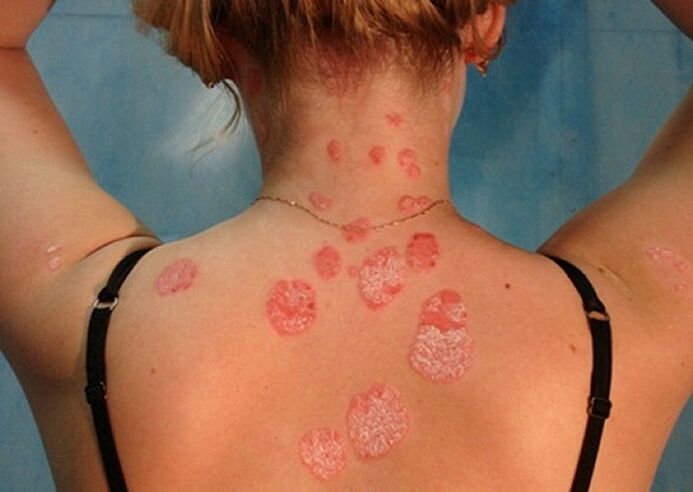
- Plaque psoriasis. . . In 90% of cases, dermatologists deal with this particular form of the disease, also known as simple or common. First, special small areas appear on the skin, raised above the level of healthy dermis. These inflamed areas are called psoriatic plaques. Gradually, they grow, joining neighboring points into a whole.
- Reverse psoriasis.This diagnosis is given to patients who develop smooth red spots on the skin folds and inside the folds - in the groin area, on the inner thighs, under the breast. Unlike simple psoriasis, the foci of inflammation are practically not covered with scales, but due to their location and constant friction, they cause serious concerns to patients. In addition, there is a risk of re-infection with streptococci or fungi, as in places where the spots are located, due to humidity and high temperature, ideal conditions are created for the reproduction of microorganisms.
- Gutate psoriasis.This type of disease got its name from the shape of the formations. The lesions are in the form of a drop, raised above the level of healthy skin. A common cause for this form of psoriasis is a previous streptococcal infection, as mentioned earlier. The point is that the patient's immunity, affected during the fight against infection, is seriously weakened - its resources are not unlimited and, like all living things, it takes time to recover - and it is against this background that an autoimmune disease is activated.
- Pustular psoriasis.It is considered the most severe form, accompanied by the formation of bubbles filled with a clear liquid. Inflammation of the skin begins around the foci, swelling and thickening appear. With a secondary exacerbation, the likelihood of which is quite high, the blisters fill with pus. Localized foci of pustular psoriasis on the arms and legs. In severe cases, there is an ubiquitous location of blisters on the body, their rapid growth and the risk of infection of the entire skin surface.
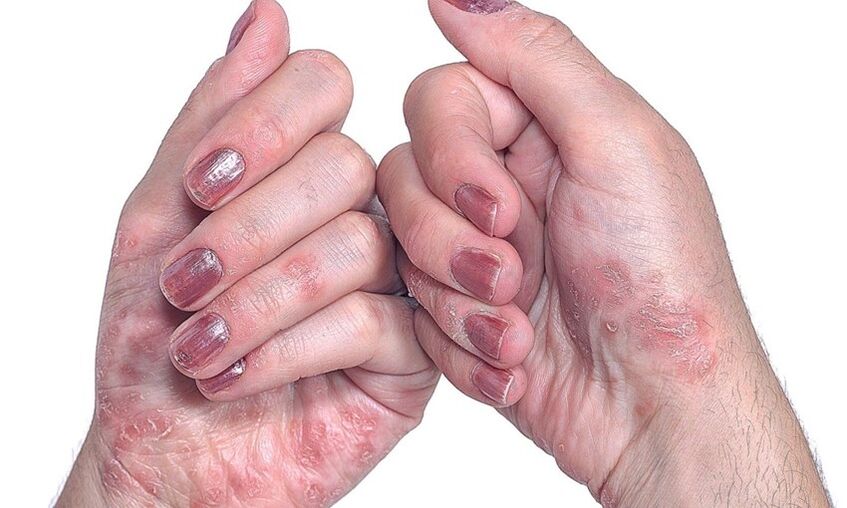
- Psoriasis on the nails.This type of disease changes the appearance and structure of the nail plates on the hands and feet. Nails thicken, lose their natural color, emit an unpleasant odor. The skin around the nail bed is thick, thick crests are formed. In advanced cases, the nails may disappear without subsequent regeneration.
- Psoriatic arthritis.In this case, the disease affects the joints and connective tissues. Most often, the inflammation affects the distal phalanges of the extremities. There is psoriatic dactylitis - swelling of the fingers. The hip and knee joints are also exposed to the devastating effects of the ongoing disease. There are frequent cases of disability with loss of ability to move independently.
- Psoriatic erythroderma.Light spots appear on the skin, while peeling of the affected layer is observed. Patients experience extreme discomfort due to constant itching and swelling. Most often, this diagnosis is made to patients who have already been treated for simple psoriasis but have not completed therapy or changed medication.
Symptoms of the disease
The first manifestation of psoriasis is a small rash on the skin. Papules grow rapidly, grow into spots 4 to 8 cm in diameter, they become more and more numerous, and dry scales form on the surface. In advanced cases, the individual spots merge with each other and the lesion affects large areas of the body. Psoriatic papules can be distinguished from other skin diseases by their round shape with clear borders, bright red or pink color and silvery white scales. They appear first in those areas of the skin, the integrity of which is compromised as a result of scratches, wounds, frostbite, constant friction. There are three characteristic signs that confirm the onset of psoriasis:
- The stearin point phenomenon- the dry particles separate easily from the affected surface, revealing an area that looks like a drop of wax or sterol.
- Psoriatic phenomena(terminal) film. Further cleansing of the papules from the scales allows you to see a transparent and moist film, the skin under which is inflamed.
- The Auspitz phenomenon. . . Removal of the terminal film leads to the appearance of smaller drops of blood on the surface of the stain.
This triad of psoriasis is unique - its presence allows an accurate diagnosis to be made without a doubt. However, different parts of the body have their own characteristics of disease manifestation.
- Psoriasis in the body.Back, neck, abdomen, thighs and lower legs are most often affected by gut psoriasis. Small papules, which resemble dots in shape, grow gradually, rising above the surface of the skin. This form of the disease is often diagnosed in people who have had a staph infection.
- Psoriasis on the hands.The most common sites for psoriatic papules on the hands are the elbows and interdigital spaces - while, as a rule, a plaque form is observed, in which small individual fragments coalesce into a single area of the lesion covered with dry scales. The forearms are less likely to be affected.
- Psoriasis of the foot.The disease begins with a single rash in the knee area. The inflamed areas bother patients with severe peeling and itching, rapidly increasing in size and merging with neighboring ones.
- On the palms and soles.In most cases, simultaneous defeat of both the palms and soles of the feet is recorded, but in some patients the disease affects the stratum corneum of the upper or lower extremities. As a result of the growth of psoriatic papules, thickening, thickening of the skin occurs with further cracking.
- Psoriasis of the head.First of all, rashes appear on the forehead, back of the head and also behind the ears. First, patients notice in themselves single scaly formations that grow, merge with those that are close together, and, over time, can affect the entire scalp. The papules itch a lot, thus causing a constant desire to scratch the skin - the resulting scars and cracks are likely to become the gateway to infection. The dried particles are separated from the pest formations - first small, somewhat similar to dandruff, and then larger flakes.
- On the face, ears, neck.Localization of psoriatic papules on the face is rather an exception to the usual clinical appearance. In rare cases, when this happens, the disease affects the areas around the eyes and eyelids, as well as the cheeks and tongue. Formations in the neck quickly spread further - to the back or to the head. The ears are the site of development of seborrheic psoriasis. Papules can appear both inside the cartilaginous shell and outside. When making a diagnosis, it is important not to confuse the disease with seborrheic eczema, which has similar symptoms.
- On the nails.There are three options for the initial appearance of psoriasis on nail plates. The first is the appearance of small dotted depressions. The second is a thickening of the nails, a change in their natural color to gray or yellow. With the further development of psoriasis of the nails, the plaque stratifies, the upper particles are easily separated. And, finally, the third is a deformation of the nail, accompanied by a loss of softness from the plate and the appearance of depressed areas.
- Symptoms of psoriasis in children.At an early age, the disease proceeds differently: the main localization of red scaly rashes are folds of skin: inguinal, in the elbow and marrow, in the neck. Papules itch a lot, children experience constant toil, become irritable and anxious. In general, all clinical variants observed in children are similar to those observed in adults. The differences have to do simply with the manifestations, the location of the pathological process and the course of the disease itself.
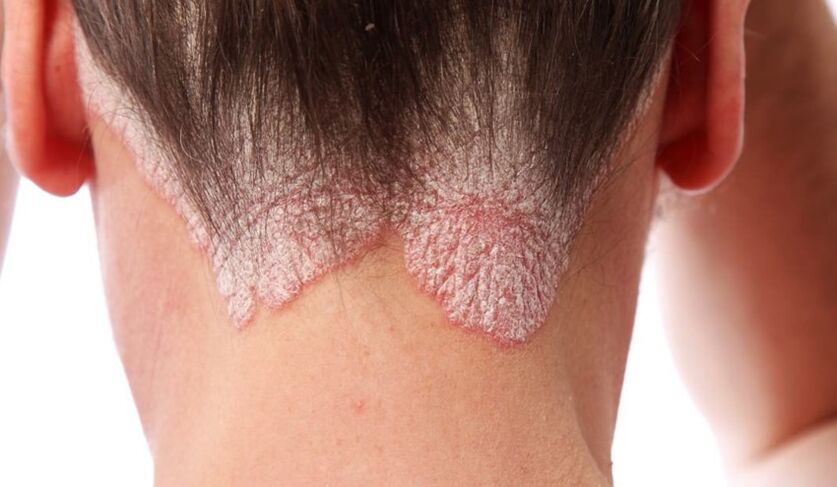
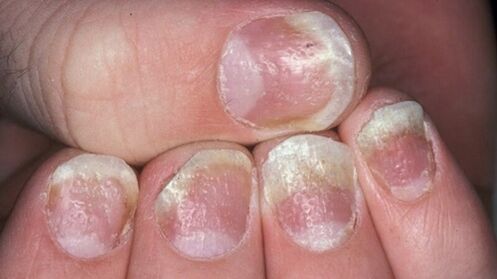
4 stages of psoriasis
Clinical dermatology, based on changes in symptoms, the degree of skin lesions, and the duration, distinguishes three stages of the course of psoriasis. However, there is an opinion that the initial stage should be recognized as another complete stage in the development of the disease.
- Initial phase.The first sign of psoriatic lesions are small rashes. The places of their appearance can be different and depend on the type of disease. Primary papules are not more than 3 mm in size, painted in a pale pink color, which after 3-4 days is replaced by a gray bloom - dead dermis particles form in place. This process is accompanied by itching and burning, and general health deteriorates. Generally, plaque formation in the initial stage lasts up to three weeks, and at this time a person has a chance to slow down the development of pathology.
- Progressive.At this stage, the disease affects important areas of the skin: for example, with normal psoriasis, plaques form, with other forms, papules characteristic of them. In the process of developing the disease, the individual spots merge with each other, covered with gray scales. The symptom that determines the progressive phase is the Köbner phenomenon (isomorphic reaction). Any skin damage after a while is accompanied by the appearance of a psoriasis rash at this site. Another confirmation that the disease is actively developing is the appearance of drops of blood, similar to dew, after the plaque is removed. The duration of this phase depends on the type of lesion. On average, it takes from two weeks to two months.
- Stationary phase.During this period, a thick gray-white or gray crust is formed. The pink rhymes disappear. The skin becomes rough, dry particles are constantly exfoliated from it. The itching and burning sensation becomes less annoying, but also does not completely disappear. New papules do not form. This stage can be quite long.
- Regressive phase.The final stage of disease development, during which there is a gradual reduction and resorption of plaques. Itching does not bother me anymore. A clear sign of regression is Voronov symptom, when the papules are surrounded by white rings. The fading of the spots occurs from the center to the periphery, as a result of which strange patterns are formed on the skin. At the end of the regressive phase, only areas of skin that are slightly different in shade from healthy areas are reminiscent of psoriasis. There is no need to talk about complete cure in the case of psoriasis. The end of the regressive phase indicates that the disease cycle is over, which can return at any time. In order to prolong remission, it is necessary to pay attention to health: avoid provocative factors, follow a diet, observe a dermatologist.
Examination plan for psoriasis
- General clinical blood test.
- Research on the content of vitamins D, B12, folic acid in the blood.
- Blood test for ALT (alanine aminotransferase), AST (aspartate aminotransferase), direct bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase, gamma-glutamyl transferase, lipid profile cholesterol, creatinine, glucose, insulin, total protein.
- Blood for rheumatoid factor, c-reactive protein, uric acid, ASLO.
- Ferritin, transferrin, serum iron are indicators of anemia (in particular, chronic diseases).
- Thyroid panels: TSH, T4 sv, TK sv.
- Co-programs.
- KhMS according to Osipov.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Traditional treatments for psoriasis
Early therapy.
The sooner a person who has detected the first signs of skin lesions visits a doctor, the more likely they are to take timely action that will prevent the disease from developing rapidly and turning into a chronic form - and, therefore, will significantly improve the overall standard of living.

One of the most commonly prescribed medications at the onset of the disease is salicylic oil. Has an anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effect, has a keratolytic effect, due to which the plaques are cleansed of keratinized particles. Naphthalene oil is also used to reduce itching.
Therapy in a progressive phase.
At this stage, an integrated approach to treatment is required and only an experienced specialist can provide it. The treatment aims at relieving the symptoms, freeing the body from toxins. To normalize metabolic processes, intramuscular injections of calcium gluconate are often prescribed. Sodium thiosulfate relieves inflammation and eliminates the manifestations of intoxication.
To moisturize inflamed skin, special emulsions and salicylic oil are used. Tools containing tar are contraindicated in a progressive stage: they act irritating and increase the patient's suffering.
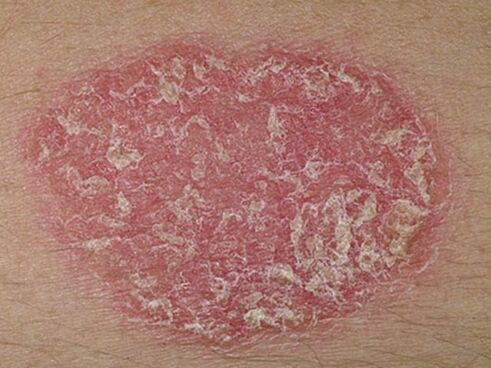
When the intensity of inflammation decreases, physiotherapy procedures can be linked. Patients with psoriasis are exposed to ultraviolet radiation, PUVA therapy, and paraffin applications. Corticosteroids and cytostatics are not used unnecessarily, these powerful drugs are needed exclusively in difficult and advanced cases.
To reduce allergic manifestations, antihistamines are prescribed and sedatives are prescribed to reduce irritability. Diuretics help reduce the swelling of inflamed skin and remove toxins from the body.
Inpatient therapy.
At this stage, the inflammation subsides, the plaques become covered with a dry crust, so funds are needed that will alleviate the discomfort from the appearance of scales. These are tar shampoo, oil-based emulsions.
In many patients, ultraviolet radiation and PUVA techniques have a good effect. If there is no improvement, doctors prescribe cytostatics.
Therapy in a regressive phase.
In the last period of the disease cycle, a continuous correction of treatment methods is required, depending on the current condition of the patient. Prevention is replacing active therapeutic actions.
The patient receives recommendations for changing diet and lifestyle in general. In order to avoid the recurrence of the skin lesion, it is necessary to avoid stressful situations that cause the formation of psoriatic plaques.
Typically, doctors give patients the following advice:
- review lifestyle: make dietary adjustments, get enough sleep, move more;
- provide normal vitamin levelsD, iron, B vitamins, protein in the body;
- normalize the digestive tract: exclude hypoacidity, impaired bile flow, SIBO and CIGR (syndromes of bacterial overgrowth and, accordingly, fungal growth);
- get rid of foci of chronic infection: clean the oral cavity, undergo treatment with an ENT doctor;
- deal with concomitant somatic pathology: hypothyroidism, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, etc.
Traditional methods to get rid of psoriasis
- Initial phase.At the first sign of skin lesions, juniper and lavender oils are effective. They soothe irritated areas of the dermis, promote the healing of minor injuries, relieve the feeling of tightness. A few drops of oil are added to a cream that is neutral in composition, for example for children, and applied to the rash that appears. Another popular method of treating the initial manifestations of psoriasis is the use of 3 percent hydrogen peroxide. Any measure, even the most harmless at first glance, can be applied after consulting a dermatologist. Diet changes, avoiding unhealthy foods and alcohol are also common recommendations of traditional healers.
- Progressive phase.In the rapidly developing stage of the disease, an infusion of celandine is added to the healing oils and hydrogen peroxide. To prepare it, you will need fresh or dried plant stalks and salted water. Alcoholic tinctures are contraindicated, they can worsen the condition of the affected skin. It is necessary to insist celandine for at least a few hours and before applying the healing solution to the tiles, treat them with birch tar.
- Stationary phase.At the stage of completing the formation of new papules, you can use popular proven methods that obviously will not harm the patient. These include the use of sulfuric oil, salicylic solution.
- Regressive phase.In the final stage of the disease course, hirudotherapy (caterpillar therapy) is often used. Although this method is not officially recognized by traditional medicine, many experts do not rule out its effectiveness. Procedures are performed within 3 - 10 days, depending on the patient's health condition.

Prevention of psoriasis: how to prevent the development of the disease
- Skin care.To minimize the likelihood of psoriatic damage in the presence of a genetic predisposition, simple ways to maintain skin health will help: water and firming procedures (bathing in the sea, baths with plant extracts and salts, contrast showers, water cleansingfresh in the air, etc. ); use of soft sponges and avoid washing covers that may damage the skin; use of detergents, with natural composition, without aggressive chemical ingredients.
- Ultraviolet rays.Several studies have proven the beneficial effect of sun exposure on skin prone to the formation of psoriatic plaques. Moderate doses of ultraviolet light help accelerate tissue regeneration and reduce inflammation. You should not abuse the sunbath: an excess of rays can provoke a worsening of the disease.
- Clothing.Synthetic fabrics, tight styles, an abundance of belts and fasteners - all this is contraindicated for patients with psoriasis, even during remission. Clothing should be natural, hypoallergenic, loose, without causing any discomfort that could lead to the return of pronounced symptoms. Dark tones should be avoided for aesthetic reasons; silver white scales are less visible on light colored clothes.
- Injuries.For patients with psoriasis, any small sores, scratches, wear and tear can cause progressive stage relapse and secondary skin infection. They must be extremely careful to avoid injuries.
- Cosmetic and household products.Not all remedies are suitable for maintaining cleanliness for people with such diagnoses. When choosing a shower gel, soap, shampoo, it is important to pay attention to their composition, giving preference to those that contain natural ingredients. It is better to buy therapeutic series of care products sold in pharmacies. Solid particle cleansers are absolutely contraindicated: they are able to start the disease process again due to minor damage to the skin. Household chemicals should also be selected based on health safety, do not use aggressive chlorine and alkali based cleaning powders. Gloves should be worn during cleaning to avoid adverse effects on the skin of the hands.
- Vitamin therapy.Maintaining vitamin balance is shown for everyone, and especially for people with chronic dermatitis. Complex preparations keep the body in good condition, help it to resist viruses and prevent metabolic disorders.

psoriasis- this is not a death sentence, but a very serious reason to review the rules you have lived by before. Your allies in the path of alleviating the disease should be competent professionals - dermatologists, nutritionists, therapists. With their help, as well as through a deliberate approach to treatment, you can learn to live peacefully, regardless of your diagnosis.